
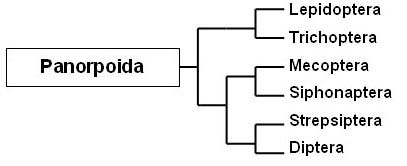
Order Lepidoptera - Butterflies, Moths (Top)
|
|
Lobocraspis griseifusa is an obligate tear drinker, thought to stimulate tear production by irritating the eye orb. Calyptra eustrigata stabs victims to form a puncture wound from which to suck blood.
Coloured scales provide the wing colours and patterns, but are easily dislodged, giving older insects a dull and worn appearance. True green is rare in adult butterflies, generally created by black and yellow scales. The green of the Green Hairstreak (Callophrys rubi) is structural and disappears if moistened.
Caterpillars and adult butterflies provide stunning examples of mimicry, including mimicry of toxic Lepidopteran species, as well as other orders of insects, and even birds and reptiles. Eyespots are commonly found on the wings, where they deflect bird attacks away from more vital areas. The purple of the Purple Emperor moth (Apatura iris) is also distracting, appearing as flashes when the light is reflected.
The division into butterflies and moths is arbitrary, with butterflies deemed to be diurnal, brightly coloured and with clubbed, threadlike antennae. Moths are generally nocturnal, dully coloured and have feathered antennae. Exceptions to confound these rules are provided by the Burnet and Tiger moths.
There are 700 - 1000m of silk in a silk moth cocoon.
Danaus plexippus, commonly known as the Monarch, Milkweed, or Wanderer butterfly, is renowned for its migration. One generation flies down North America to overwinter in Mexico, then reproduces in spring and dies, leaving their offspring to begin the journey northwards. A number of generations complete the return to the north over the rest of the spring and summer, coinciding with the flowering of milkweed.
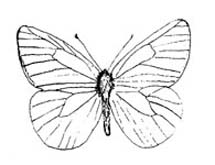
Order Trichoptera - Caddisflies (Top)
|
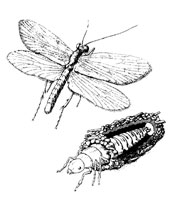  |
Order Mecoptera - Scorpion flies, Dance flies, Hanging flies (Top)
|
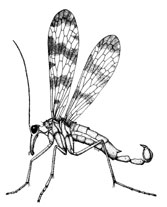  |
Although currently represented by only 500 species, Mecoptera made up a large part of the fauna of the Lower Permian era, and are the oldest fossil endopterygotes known.
Mecoptera are preyed on by spiders whilst on the webs collecting nuptial gifts, but seem to be able to repel the spiders by regurgitating onto the webs and themselves.
Order Siphonaptera - Fleas (Top)
|
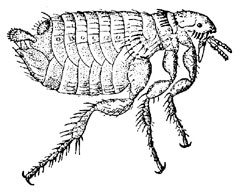 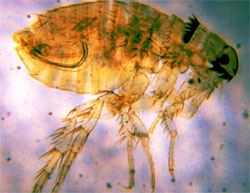 |
Fleas are not host specific, despite being named after a host on which they are found. The human flea, Pulex irritans, occurs on at least 7 different mammals, and, in turn, 19 different species of flea have been found on humans.
The largest flea is Haemaropinus schefferi, found on the world's most primitive rodent Aplodontia rufa, the mountain beaver (which doesn't live on mountains and isn't a beaver). Now nicknamed the Super Flea, H.schefferi measures 9mm.
The record flea jump is 34 cm by the cat flea Ctenophalides felis.
Order Strepsiptera - Stylopids,Twisted-wing Parasites (Top)
|
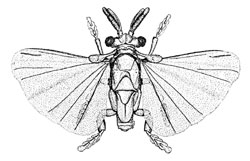 |
A high degree of specialisation has made it difficult to place the Order Strepsiptera phylogenetically, and it has been linked to the Hymenoptera, Diptera and Coleoptera. Most recent evidence puts forward strong arguments for its position as a sister group to the Diptera. (Whiting et al 1997, Systematic Biology 46,1-68)
Males are only active for a few hours, during which time they detect the female's pheromone using their unusual antennae, and trace her to her host. Only a small part of the female protrudes, enough to breathe, mate and lay eggs.
Order Diptera - True Flies (Top)
|
Suborder Nematocera
|
  |
Suborder Brachycera
|
  |
Suborder Cyclorrapha
|
  |
What do you call a fly with no wings? A sheep ked, a Deer fly... or a walk.
Blowfly larvae are used in medicine as they eat only dying flesh, and secrete antibiotics which improve healing times.
Diptera are important as carriers of malaria, yellow fever, river-blindness and many other diseases.
The Forcipomyia midges have the fastest wingbeat of all insects, at 62760 per minute (1046 per second,) which is also the fastest muscle movement ever recorded.






